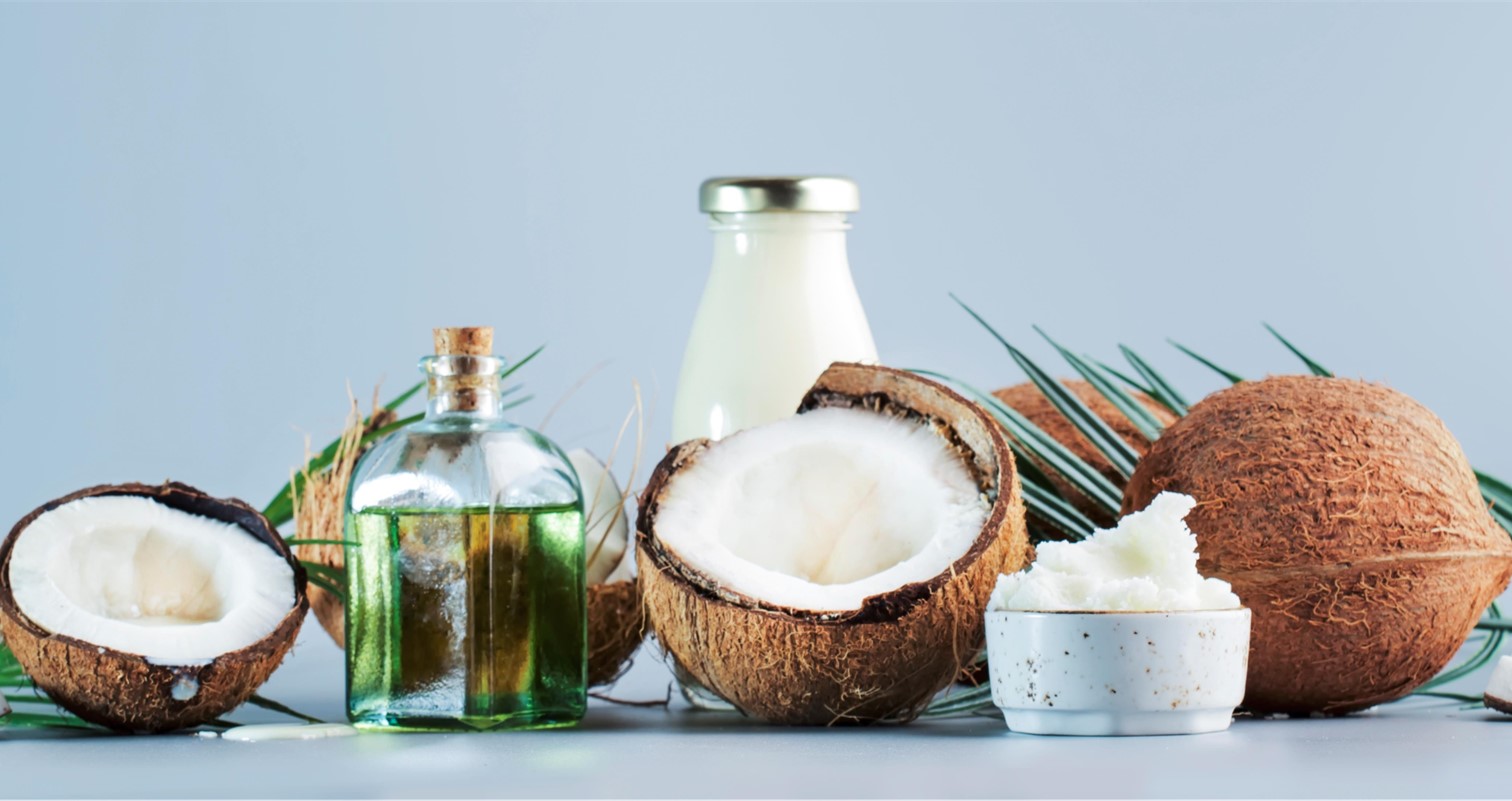
MCT – The fatty acids that are beneficial to your health
You have probably heard of MCTs in sport supplements or athlete foods, but what are MCTs and which benefits do they offer?
What are MCTs and where do they come from?
MCT stands for “medium chain triglycerides” and are fatty acid esters with 6 to 12 carbon atom chains, which include hexanoic acid (6 carbon atoms, also known as caproic), octanoic acid (8 carbon atoms, also known as caprylic), decanoic acid (10 carbon atoms, also known as capric) and the 12 carbon atom MCT, known as lauric acid1.
Palm oil and coconut oil are the main sources of MCT, since they contain them in high concentrations of up to 60% of the total fats in them. Additionally, some recent studies have shown the presence of MCTs in milk fat, and even in plants such as the Camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora).
What are the benefits of Medium Chain Triglycerides?
One of the main reasons why MCTs have so many benefits for your body is due to their size, which, when compared to other fats, is much smaller, which enables them to be processed and absorbed more easily, in addition to being less prone to be stored in the body, since they pass directly from the intestine to the liver, where they break down to be used as immediate energy.
MCTs are an excellent alternative for people following a keto diet. It has been demonstrated that these oils accelerate ketogenesis and reduce the adverse effects of this type of diet, improving the tolerance to very low-carb diets.

There is also evidence that MCTs can help lose weight, since their almost-immediate metabolization induces satiety much faster than other fats. Recent studies have analyzed the effect of MCTs on appetite hormones; however, the results still require further research1.
It is also suggested that it offers benefits to athletes, reducing the level of lactic acid in the blood, which accumulates during physical activity increasing muscle acidosis and decreasing physical performance4.
Furthermore, MCTs have hypocholesterolemic properties, leading to a reduction in cholesterol by reducing its absorption in the small intestine and fostering its excretion. Additionally, its gastrointestinal benefits have been thoroughly studied—there are studies that show that these triglycerides reduce the intestine’s inflammatory response and improve the intestine microbiota and permeability, improving the intestine’s metabolism, which is beneficial when treating disorders such as Crohn’s and Celiac disease, which are largely associated with the intestines’ inflammatory response6,7.
MCTs have also recently been strongly linked to improvements in neurological disorders, in illnesses such as epilepsy and in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, due to the neuroprotective effect of ketone bodies, which are mostly generated by MCT-rich diets, in addition to the capabilities of caprylic and capric acid which, unlike other triglycerides, can cross the blood-brain barrier and act as a source of alternative energy for neurons and astrocytes8.
MCT, the next functional ingredient
In its article focused on MCT oils of March this year, Mintel states that there are great opportunities for brands to increase the use of this ingredient beyond the realm of sport supplements and Keto diets, and that it is becoming increasingly widespread as an ingredient to boost energy and enhance brain performance, positioning itself as the next big functional ingredient in foods and drinks9.
Concept of dieting. Young woman with slim body type and in yoga clothes is at home. In the United States, the level of interest for MCTs rose to 31% and 34% for Gen Z and Millennials, respectively, and the market is expected to grow by approximately 256 million dollars at a compound annual growth rate of almost 7% during the 2020-2024 period10
MATHIESEN FOOD offers innovative, safe ingredients for the food industry, including in our portfolio functional ingredients such as the attractive MCT oil, DHA, fibers and collagen peptides, among others, to address new consumer demands.
Below are a few examples on the market and presentations through which you can consume these triglycerides that are so beneficial to your health.
- Almond and hazelnut drink, which contains 1.5% of MCT oil (Thailand).
- Protein energy bar with 3% MCT oil (Poland).
- MCT-rich coconut oil (Chile)

To learn about our functional food ingredient portfolio, contact us and one of our experts will get back to you promptly.
Bibliography:
- Nimbkar, S., Leena, M. M., Moses, J. A., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2022). Medium chain triglycerides (MCT): State-of-the-art on chemistry, synthesis, health benefits and applications in food industry. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety, 21(2), 843–867.
- McCarty, M. F., & DiNicolantonio, J. J. (2016). Lauric acid-rich medium-chain triglycerides can substitute for other oils in cooking applications and may have limited pathogenicity. Open heart, 3(2), e000467.
- C Harvey, C. J., Schofield, G. M., Williden, M., & McQuillan, J. A. (2018). The effect of medium chain triglycerides on time to nutritional ketosis and symptoms of keto-induction in healthy adults: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2018. 2630565.
- U: Nosaka, N., Suzuki, Y., Nagatoishi, A., Kasai, M., Wu, J., & Taguchi, M. (2009). Effect of ingestion of medium-chain triacylglycerols on moderate- and high-intensity exercise in recreational athletes. Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology, 55(2), 120–125.
- Li, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Xu, Q., Zhang, Y., Xue, C., & Guo, C. (2018). Medium-chain fatty acids decrease serum cholesterol via reduction of intestinal bile acid reabsorption in C57BL/6J mice. Nutrition & metabolism, 15, 37
- Heydinger Galante, J. (2020). Medium-chain oils. Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 1–14.
- Rial, S. A., Karelis, A. D., Bergeron, K., & Mounier, C. (2016). Gut microbiota and metabolic health: the potential beneficial effects of a medium chain triglyceride diet in obese individuals. Nutrients 8, 281.
- Augustin,K., Khabbush,A., Williams, S., Eaton, S., Orford,M., Cross, J. H., Heales, S. J. R., Walker, M. C., & Williams, R. S. B., (2018). Review mechanisms of action for the medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet in neurological and metabolic disorders. Lancet Neurology, 17, 84–93.
- Ingredient watch: medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil. Mintel: Global Market Research & Market Insight. 28/03/2022
- Technavio. (2020). MCT Oil Market Analysis Highlights the Impact of COVID-19 2020–2024| Demand for Natural Products to boost the Market Growth | Technavio | Business Wire.