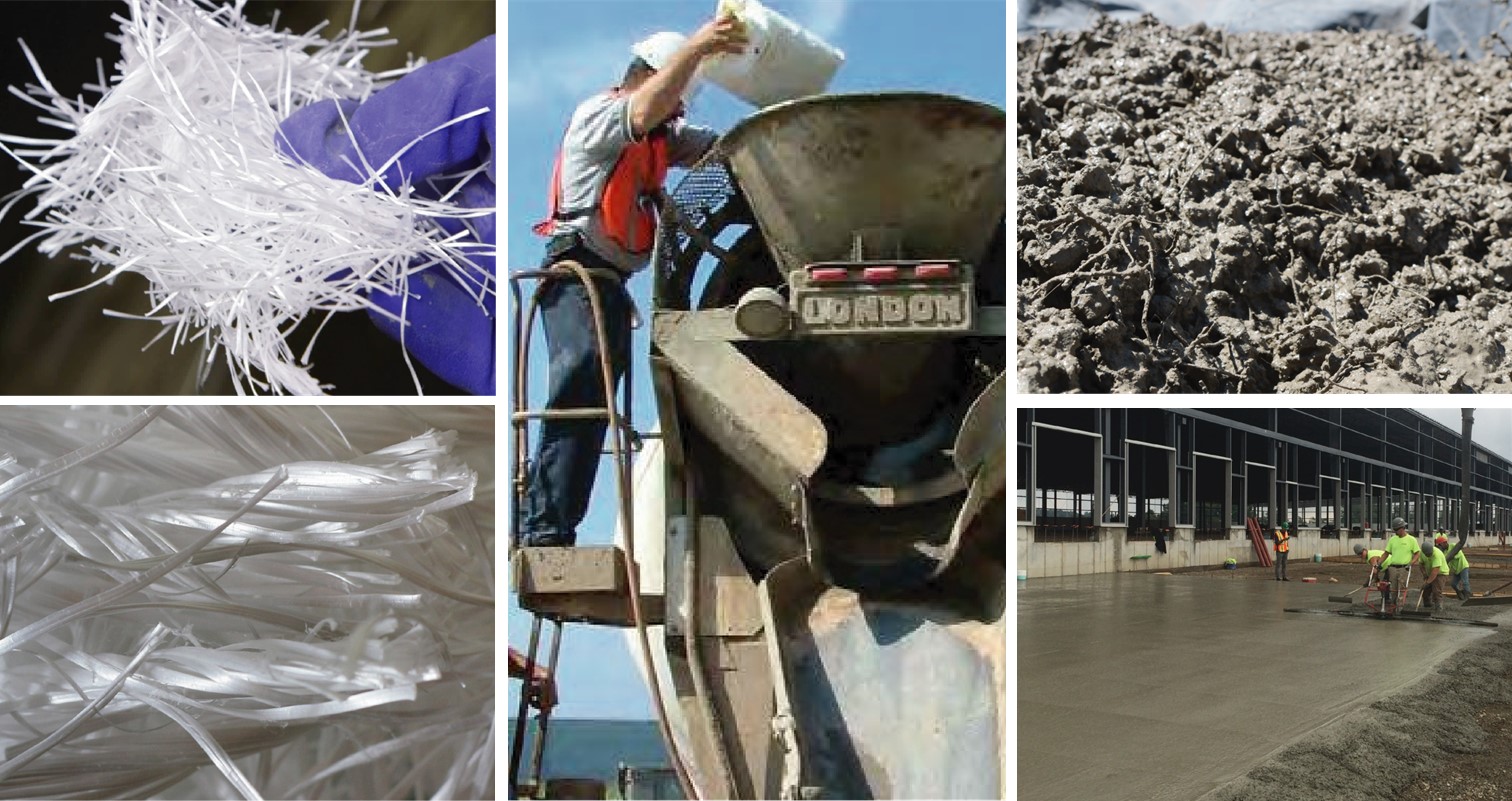
Macro Synthetic Fibers in Concrete Mixes: Usage and Benefits
Macro fibers used in concrete mixes in construction have been a significant innovation that has revolutionized the way structures are designed and built. These fibers, consisting of a blend of polypropylene/polyethylene, self-fibrillate when incorporated into the concrete mix, enhancing its mechanical and structural properties and can be successfully used to replace welded wire mesh and metallic fibers in a wide variety of applications.
Key Applications:
- Precast concrete elements.
- Shotcrete (tunnel lining, pool construction, slope stabilization).
- Pavements and Whitetopping.
- Concrete floors in distribution centers, industrial floors, warehouse floors.
Key Benefits:
- Increased Ductility: Macro fibers increase ductility in tensile and flexural stresses of concrete, allowing for more deformation capacity without collapsing, resulting in a more durable structure resistant to dynamic and static loads. This is especially useful in pavements, supported slabs, and vertical structural elements subjected to heavy and seismic loads.
- Crack Control: The addition of macro fibers helps control and reduce crack formation in concrete, significantly improving the durability and service life of the structure. This is crucial in applications where cracks can compromise the integrity of the structure, such as industrial floors or retaining walls.
- Improved Toughness: Fibers provide toughness to concrete, meaning it enhances its ability to resist impacts and cyclic loads. This is essential in structures exposed to severe weather conditions or repeated impacts, such as outdoor pavements or maritime infrastructures.
- Shrinkage Reduction: By adding macro fibers to concrete, hydraulic shrinkage is reduced, minimizing the risk of cracking and allowing for the reduction of crack width. This is essential to prevent structural damage due to durability issues and maintain the integrity of the construction over time.
- Others:
- Mitigates plastic shrinkage and shrinkage cracking, reduces segregation and bleeding.
- Improves surface wear resistance.
- Excellent increase in fatigue resistance in pavement cases.
- Increases adhesion of elements such as pavers, porcelain tiles, among others.
- Provides three-dimensional structural support.
- Reduces fiber content and optimizes thickness compared to metallic fibers for shotcrete application.
- Excellent dispersion in concrete.
- Reduces equipment wear compared to steel fibers.
- Reduces rebound of shotcrete compared to steel fibers and other synthetic fibers.
- Avoids doubts about correct locations of conventional meshes and reinforcements.
- Dismisses concerns regarding the “shadow effect” on the backside in the case of shotcrete on welded wire meshes or traditional reinforcements.
- Non-corrosive.
- Reduces CO2 emissions by more than 50% compared to welded steel meshes.
In summary, fibers in concrete mixes represent a very relevant added value to improve the strength, durability, and service life of structures under construction. Their widespread use is transforming the construction industry by offering more efficient and sustainable solutions for a variety of structural applications.
Mathiesen brings TUF – STRAND SF to Uruguay, Bolivia, and Paraguay, a Euclid Chemical Brand.
TUF – STRAND is a blend of polypropylene/polyethylene macro synthetic structural fibers, which self-fibrillate when incorporated into the concrete mix, successfully used to replace welded wire mesh and metallic fibers in a wide variety of applications.
TUF – STRAND SF fibers:
- Comply with ASTM C-1116 standard, specification for fiber-reinforced concrete and shotcrete, and are specifically designed to provide tensile strength equivalent to conventional reinforcements.
- Comply with applicable parts of the International Code Council (ICC), acceptance criteria AC 32 for synthetic fibers, have UL certification for use in metal deck construction systems, and are recognized by ACI 360 R-06 and SDI/ANSI.CI.O as alternatives to welded wire mesh reinforcement.
- TUF-STRAND has been tested according to ASTM C-1399, C-1550, C-1609, and C-1018.