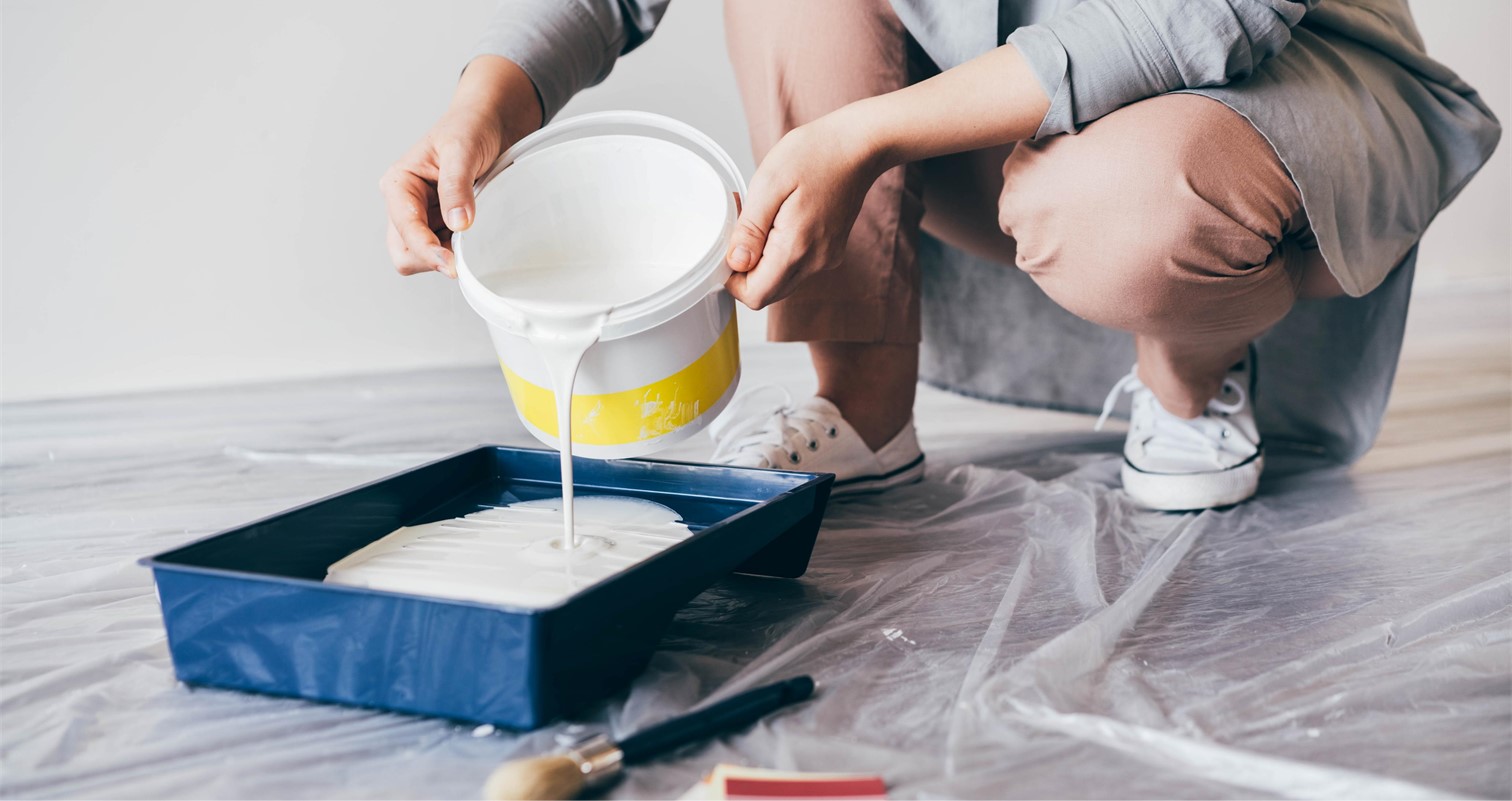
Cellulosic thickeners: 7 tips for using them in paints
When formulating or designing paint, you need to dedicate some time to its rheological system, and cellulose ethers or cellulosic thickeners play a major role in this regard.
But, what are cellulose ethers?
Cellulose is the main component of wood, paper and cotton, and when subjected to an etherification reaction, the secondary hydroxyls of cellulose are replaced by ether groups such as methyl, hydroxypropyl and other groups, which ultimately form different varieties of cellulose ethers. There are many options, meaning that there are also many applications and characteristics that can be obtained. Therefore, choosing the right cellulosic thickener usually requires previously analyzing the product, its processing conditions and final use. Generally, its most common and documented uses include paint, mortar, food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Use of cellulose ethers in paint
Cellulosic thickeners are widely used in water-based paints as a set of additives that modify their rheological behavior, which also depends on many variables.
Being able to control the flow’s behavior and the formation of films guarantees a greater success in regard to the perception of performance, aesthetical appearance and ease of application. The paint manufacturer must study and control characteristics and phenomena such as:
- Sedimentation.
- Leveling.
- Splash.
- Time opened.
- Viscosity.
Recommendations for choosing the right cellulosic thickener for your paint
The following must be considered when choosing the right type of cellulosic thickener that takes into account the variables mentioned above, as well as the interaction with other components of the formulation and the environmental conditions and methods of application:
- Knowing and controlling the right pH during manufacturing and in the final product; this is because the solubility of these ethers changes based on the pH, and therefore the processing times and/or activation ease will not remain the same.
- Clearly defining the target behavior of the final product, the budget and the rheological features of its materials.
- Knowing whether its cellulose ether is of delayed solubility or if it immediately reacts by forming clumps in the presence of water.
- Controlling the addition rate.
- Analyzing the need for protection against enzymatic action.
- Taking into account the ability to modify the time it remains open; this affects the formation of film and the proportion of other additives that generate VOCs.
- Lastly, understand that viscosity affects the dispersion processes and the ultimate stability of the paint.
At Mathiesen Group we offer a complete line of cellulose ethers and cellulosic thickeners for the Paint, Dye and Adhesive sector, which are available in a wide range of viscosities and characteristics to guarantee your satisfaction across different applications.
Contact us and we will gladly offer you advice to choose the cellulosic additives (or others) that are most suitable to address the specific requirements of your formulation.